Until finally, with the setting in of the year 2025, noticeable slowdown signals began to creep into global manufacturing and raised a host of concerns among economists, policy thinkers, and industry leaders. One question remains after years of volatility induced by the pandemic, supply chain disruption, surges in inflation, and geopolitical tensions: is the world inching toward a new era of sustained contraction in manufacturing?
It considers what drives the trend, general patterns around the world, and some of the possible implications.

The Current State of Global Manufacturing
a. Falling factory output in the major economies
Output is shrinking in a variety of industries in the United States, China, Germany, Japan and South Korea. For many regions, readings for purchasing managers’ indexes have stayed below 50, signaling contraction, not growth.
b. Weakening New Orders and Export Demand
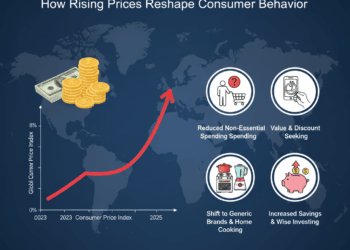
Worldwide demand for consumer goods, electronics, and industrial machinery has cooled. Economies dependent on exports are feeling the pinch more acutely than other countries now as international orders decline on account of :
- Sluggish consumer spending
- High interest rates
- Currency instability
- Changes in international trade routes
c. Inventory Overhang
Fearing a shortage, companies overstocked during the post-pandemic recovery; now, warehouses remain full, and businesses are reducing production to work through excess inventory.
What is driving the contraction trend?
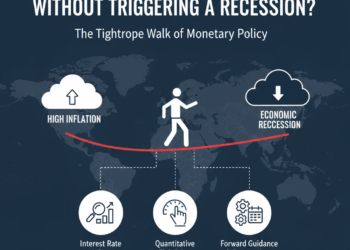
a. Prolonged Inflation and High Interest Rates
Although the inflation rate is cooling down, the prices are still high in many countries. Central banks keep higher interest rates that :
- Reduced consumer spending
- Increase the cost of borrowing for firms
- Slow investment in new factories and equipment
The tight monetary environment suppresses manufacturing demand sharply.
b. Shifts in Global Supply Chains
Companies are leaving China for Southeast Asia, India, and Mexico. This “fragmentation” is supposed to build resilience, but it is disruptive to existing ecosystems of production and increases short-term costs.
c. Geopolitical tensions and trade barriers
Ongoing conflicts, sanctions, and shifting alliances are reshaping trade flows. At the same time, tariffs, export controls, and economic security policies make global manufacturing operations less efficient across borders.
d. Automation Reducing Labor Demand
Automation increases to compensate for the higher wages and labor shortages, but in so doing it slows job creation in manufacturing. But whereas automation raises productivity, it does not necessarily increase factory output during periods of weak demand.

Signs the Manufacturing Sector Might be Headed for a Long-Term Slowdown
a. Falling Investment in Physical Production Capacity
Firms are becoming more and more reluctant to invest in new plants or large machinery. Instead, the capital spending is increasingly being channeled into :
- Software
- Robotics
- AI-systems
- Data integration
The emphasis is no longer on physical expansion.
b. The Rise of Services Over Goods
We’re living in an increasingly service-oriented world, with people spending more on things like travel, digital services, and experiences rather than physical goods, according to estimates.
c. Structural demographic changes
Additionally, these aging populations in advanced economies contribute to a reduction in labor availability and, ultimately, domestic consumption of manufactured goods.
Meanwhile, younger populations in emerging markets lack the purchasing power that would offset weakening demand in richer countries.
d. Sustainability and Environmental Regulations
Stricter climate policy will, in turn, compel companies to reform operations and increase costs over the coming years. Companies will be compelled to invest in cleaner technologies that decrease their own emissions and meet environmental standards, which will dampen the growth rate in new production capacity.
Does This Imply Permanent Contraction?
Not necessarily, since even if the slowdown is real it may reflect a metamorphosis rather than a decline that is permanent in nature.
a. Manufacturing Is Evolving, Not Disappearing
Factories are getting smarter, cleaner, and more automated. Advanced manufacturing such as semiconductors, components for electric vehicles, and renewable energy equipment is in strong demand.
b. New supply chains will create new growth opportunities.
Other countries that could see manufacturing growth include India, Vietnam, Indonesia, and Mexico, as companies continue to seek diversification.
c. Green Manufacturing Could Drive Future Expansion
As the world shifts toward renewable energy and greener technologies, new industries will replace the old, more carbon-intensive production.
Regional Views: Where Contraction Bites Hardest
a. China
A continued export contraction, reduced domestic demand, and rising competition from Asia are contributing to the structural slowdown in China’s manufacturing sector.
b. Europe
From Germany to Italy, European factories are being tested by high energy costs, regulatory pressure, and weak consumer demand.
c. United States
It is thus contracting in its more traditional sectors and expanding in semiconductors, aerospace, and electric vehicles; in the latter areas, there is strong industrial policy support.
d. Emerging Asia
While countries like Vietnam and India are getting new investments, their capacity to absorb this global shift remains limited.
Outlook for the Future: 2025–2030
a. Short-Term Outlook : Continued Weakness
Manufacturing output probably will be subdued in light of high interest rates, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical fragmentation.
b. Medium-Term Outlook: Selective Industry
Growth Sectors set to grow will include :
- Renewable energy technology
- Robotics and automation
- Semiconductors
- Electric vehicles and batteries
- Medical devices
c. Long-Term Outlook : A More Balanced Global Supply Chain
Manufacturing may stabilize by the end of the decade, as new regional supply chains mature and global demand adjusts to new economic realities.
Conclusion
Undeniably, global manufacturing is under pressure, and this recent contraction signals a fundamental transition that’s happening in the world’s economy. But that does not mean this decline is permanent. Rather, the manufacturing sector is shifting to another phase characterized by automation, regional diversification, and shifting demand. The difference between whether it is a long-term contraction or a short-term adjustment lies with how governments, businesses, and workers adapt to the changing global landscape.